Dr. Yuan talks about diamonds: the macro and micro structure of diamonds.
Release time:
2021-12-29 00:00
Macro-structure of diamonds
Using the synchrotron radiation device of the Beijing Electron Positron Collider, the electron beam is first accelerated to a high-energy electron beam current by a linear accelerator, and the electron beam is cyclically moved at a high speed in a storage ring with a circumference of 240.4 meters, the speed reaches the speed of light, and the synchrotron radiation X-ray is led to the outer test station along the tangential direction, the film is perpendicular to the incident ray, and the white light morphology can obtain the derivative image of multiple crystal face groups in a few seconds. However, the synchrotron radiation equipment cannot be used easily, and a small X-ray machine can also be used to irradiate the sample, but it takes tens of minutes to get photosensitive, and the derivative images of multiple crystal face groups are also obtained on the negative. The derivative images of each crystal face group are orderly arranged in the direction of the main crystal face, and the degree of symmetry of arrangement shows the angle difference between the facet and the main crystal face, for example, the (100) surface is a square structure, the (111) surface is a triangular/hexagonal structure, and the (110) surface is an elliptical structure. The following figure:
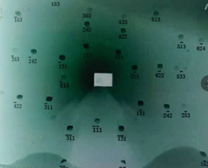

Correct angle of main crystal plane (100) plane Slightly off angle of main crystal plane (100) plane, acceptable
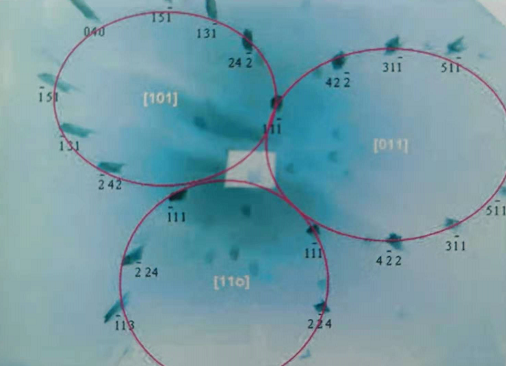
The main crystal plane (111) is arranged in three symmetrical circles. The correct angle is slightly off the main crystal plane (111), which is acceptable.


The picture on the left shows the multiple sets of crystal plane derivatives in the direction of the main crystal plane (110) of natural brown diamond. It is arranged at the correct angle of symmetrical ellipse. After the growth of brown diamond is completed, it is subjected to great pressure under the ground. The two enlarged figures on the right are plastic deformation caused by extrusion and crushing of the two crystal plane groups.
The microstructure of diamonds
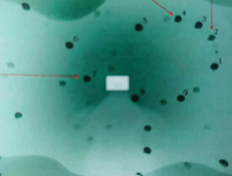
Using a transmission electron microscope, a diamond can be magnified tens of thousands to millions of times, and an image of carbon atoms can be seen. It is very difficult to make the sample. First, the diamond is ground to a thin sheet of 10-30 microns, then the argon ion is thinned to the central penetration, and the thickness is gradually increased to 2000Å around. Microstructural defects, atomic lattice images and atomic images in the diamond sheet can be seen in the transmission electron microscope.
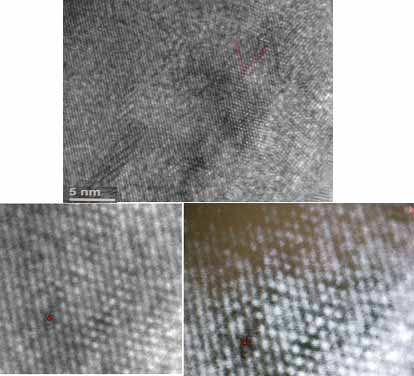
The thin slice sample after argon ion thinning, the black on the left is the penetrating part, and the edge color is the thickening part
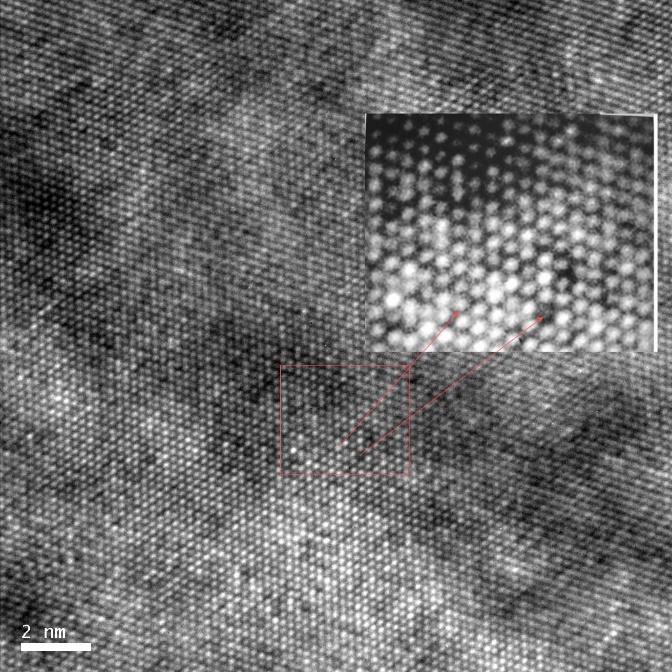
Diamond lattice fringe image [111] and atomic image, each dot is a carbon atom, magnified 1 million times under transmission electron microscope
transmission electron microscopy features:
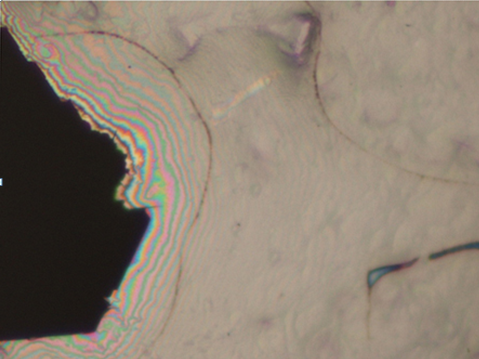
To observe the extremely small impurities in diamonds, it is necessary to thin the diamond to a few microns in thickness and use a transmission electron microscope to magnify it thousands, tens of thousands to millions of times. The test was completed at 300KV using TECNAI F30 Field Emission Transmission Electron Microscope (FEI) of the Institute of Physics, Peking University. The results as shown in the following figure show that when CVD-grown diamonds grow at a fast rate, it is very easy to have carbon atoms that are not converted into SP3-structured diamonds, but remain in the growing CVD-grown diamonds in the impurity state of SP1, SP2 carbon or graphite. Because the volume is very small, it can only be magnified by TEM of thousands to ten thousand times, and black graphite inclusions, equal inclination lines and dislocations can be seen.
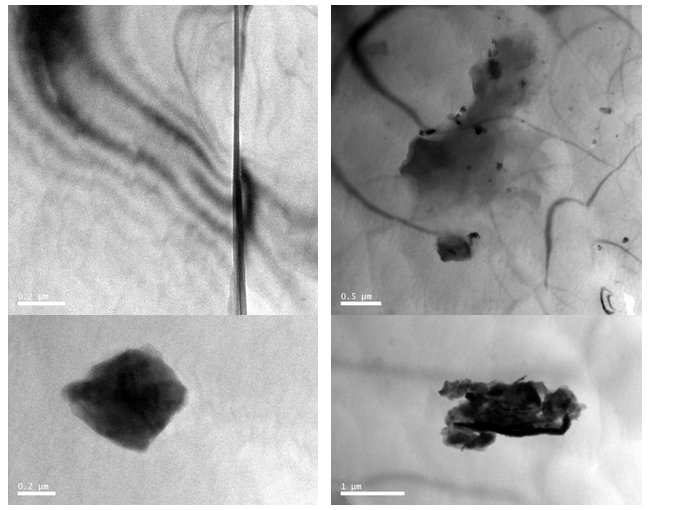
Black graphite inclusions, isoclinations and dislocations can be seen in CVD grown diamonds under transmission electron microscopy.
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) studies the structure of high temperature and high pressure (HPHT) diamond is imperfect, there are dislocation loops and dislocation couples, which are derived from the presence of supersaturated vacancies and internal stresses and inclusions in diamond.

The Equal Inclination and Dislocation Pair of HPHT Synthetic Diamond with Radiation-Modified Deep Red
Previous Page
Related News
To participate in the "2011 Beijing International Lighting Exhibition" exhibition held in Beijing
Participate in the "7th Guangzhou International LED Exhibition (LED CHINA 2011)" exhibition held in Guangzhou
To participate in the "Japan International Electronic Products Exhibition" held in Tokyo, Japan"
Participated in the "Twelfth China International High-tech Achievement Fair" held in Shenzhen and won the "Excellent Product Award" certificate
Yuan Dong was invited to give a lecture at the Appraisal Institute of Taiwan Gemological Institute.
Dr. Yuan Zhizhong, Chairman of Bench Diamond Technology, gave a lecture entitled "Identification of Gem Diamonds Cultivated by CVD Method" at the Appraisal Institute on the 11.9 at the invitation of the Appraisal Institute of Taiwan Gemological Institute. In the lecture, Yuan Dong introduced in detail the historical principles of CVD diamonds and their development status, and introduced in detail several methods to distinguish CVD diamonds from natural diamonds on how to identify gem-grade CVD diamonds that participants are concerned about! Yuan Dong's wonderful speech was well received by the participants!
Yuan Dong Attends the Symposium at the Invitation of Hangzhou Jewelry City
Dr. Yuan Zhizhong, Chairman of Bench Diamond Technology, was invited by Hangzhou International Jewelry City to attend an academic symposium on November 19, 2013. At the symposium, Yuan Dong gave a speech entitled "International Situation and Identification of CVD Synthetic Diamonds" on the current situation of CVD synthetic diamonds that jewelers are concerned about and how to distinguish CVD diamonds from natural diamonds. In the speech, Yuan Dong introduced in detail the history of CVD diamonds, the international situation of CVD diamonds and the commonly used identification methods of CVD diamonds, and answered some questions raised by jewelers. Mr. Yuen's speech was well received by the participants, and all jewelers said they benefited.

