Dr. Yuan's Lecture on Diamonds: Difficulties in Cultivating Diamond Classification Certificates
Release time:
2021-09-29 00:00
Whether the concept of diamond identification certificate grading is correct is related to whether the grading given on the certificate is reasonable. The grading items of diamond identification grading certificate are: color, clarity, lathe work (angle ratio), polishing, symmetry.
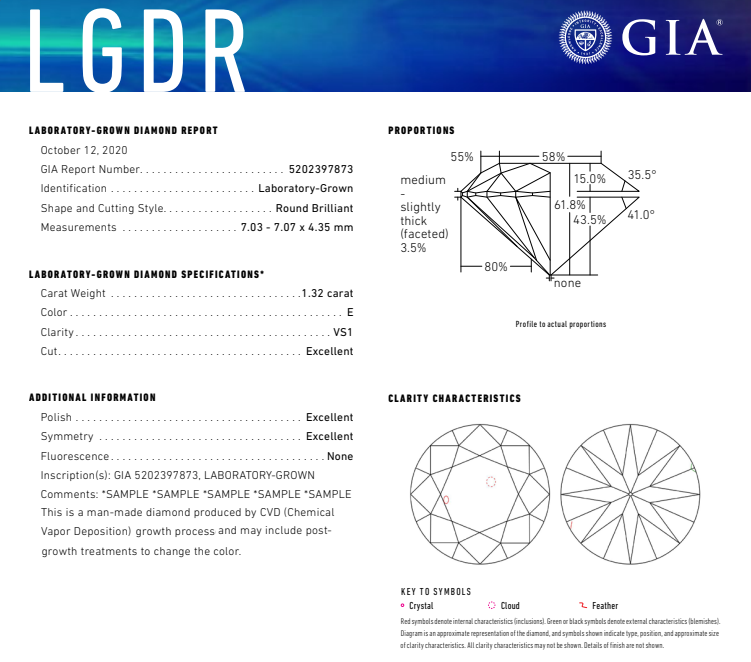
Figure 1,GIA Grow Diamond Certificate Sample
1. Turning, polishing and symmetrical grading
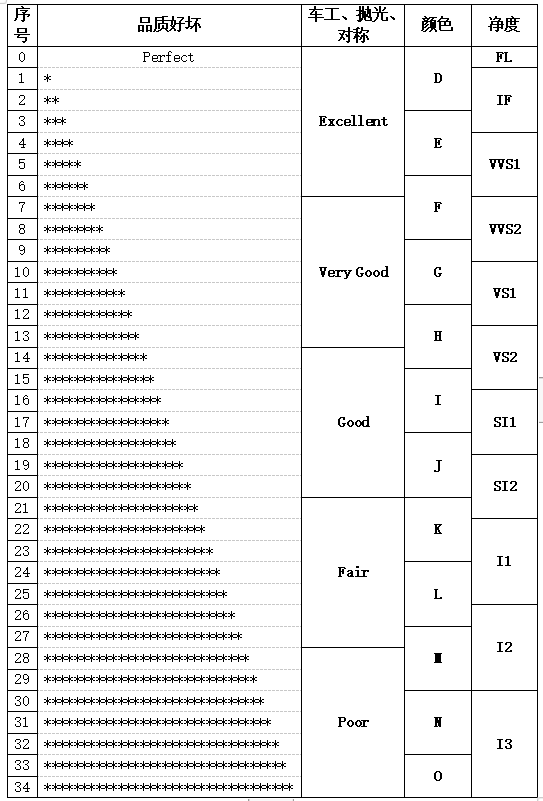
The lathe work (angle ratio), polishing and symmetrical grading of diamond identification are divided into: excellent, very good, good, fair and poor. The principle of all identification and grading is to divide all possible qualities from the most perfect to the worst into dozens to hundreds of different situations, then take the best 1/5 as excellent, the second best 1/5 as very good, and divide them into good, fair and poor again according to the ratio. Therefore, from the most perfect perfect to the lowest position of the excellent, there is a range, not the entire excellent range, which is perfect, as shown in the following table:
Table 1, the principle description of each grading item of the identification grading certificate.
2. Color grading
The principle of color grading: put a lot of diamonds of different colors from the whitest in the first position, put the ones that are a little worse than the whitest in the second position, and then arrange them to the darkest Z in sequence. After arrangement, call the first part D. The range of D is not only the colorless and transparent perfect of the first place, but also the range of D will drop several grains. This paragraph is called D. Then the following grains of D will be customized E and arranged in sequence to Z before the color. There are a total of 23 color grades, so everyone should have the idea that the color of D is not just the whitest one.
3. Clarity classification
The same is true for clarity from the cleanest flawless Flawless inside and outside to the worst Pique3. At the earliest time when GIA determined the clarity, it was defined as a flaw only when it could be seen by a trained appraiser with a ten-fold magnifying glass, not with a high-power microscope. Therefore, the best FL is flawless inside and outside, and no flaw can be seen inside and on the surface with a ten-fold magnifying glass, even FL, but it cannot be seen with a ten-fold magnifying glass, and it can be seen with a 20-40-fold or 60-fold microscope, it is not a defect. This is a very basic rule. In fact, a regular appraisal company will use a 20-fold microscope to carefully find out all the defects, and then replace it with a 10-fold microscope to observe whether the defects can be seen. If not, it is not a defect. Similarly, the series of judging polishing and symmetry are also magnified by a ten-fold magnifying glass (the actual appraiser uses a microscope) for grading.
4. Excellent/Eight Heart and Eight Arrows
There is a considerable difference between the Excellent standard in the turner ratio and the standard of the eight hearts and eight arrows. The eight hearts and eight arrows only account for a very small part of the Excellent range. In fact, the angle ratio of the Excellent range is very clear and not good. Figure 2 is the standard of eight hearts and eight arrows, and Figure 3 and Figure 4 are optional cases in the Excellent.
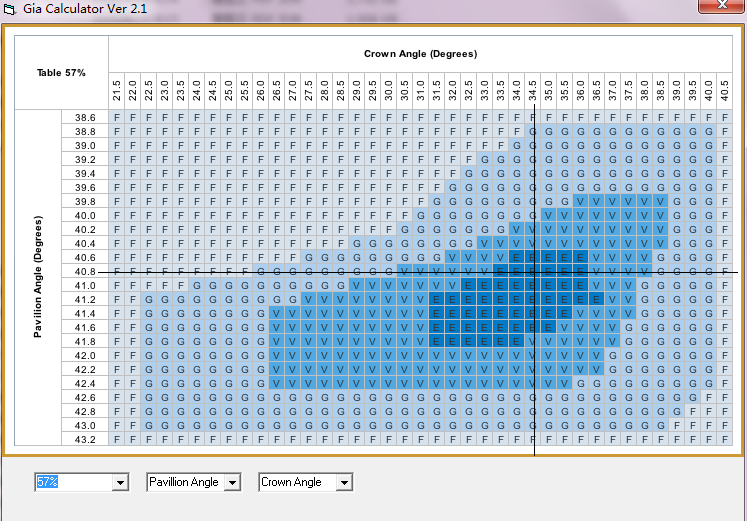
Fig. 2, eight hearts and eight arrows lathe worker, 57% table top, crown angle 34.5, bottom angle 40.8
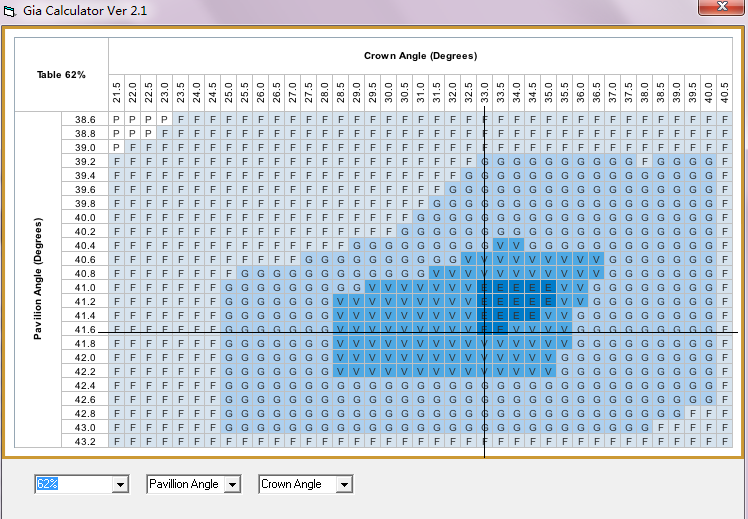
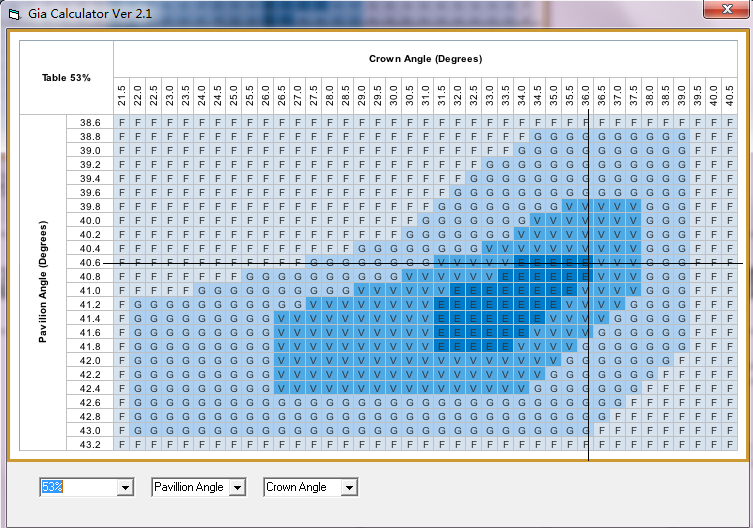
Figure 3,Excellent lathe man, Figure 4,Excellent lathe man,Table top 62%, crown angle 33, bottom angle 41.6, table top 53%, crown angle 36, bottom angle 40.6
5. Characteristics of GIA and IGI Identification Sub-offices
Diamond identification and grading certificates were formally implemented by GIA in the United States in the 1950 s. They defined color grading standards and tools, tools and methods for clarity grading, and standards for lathe work (angle ratio), polishing and symmetrical grading. Only the turners (angle ratio) have quantitative data specifications for these five grades, and the other four are subjective visual judgments of appraisers, so the personal subjective judgments of different appraisers will be quite different. The appraisers of the same appraiser are easy to integrate the subjective judgment standards. The appraisal branches of different countries and regions have not been trained and graded according to unified standards. As a result, the grading results of each branch will be quite different, in particular, some appraisal system branches are joining methods, and the hosts of each branch have their own interests. Therefore, the appraisal and grading results of each branch are more different. Based on the experience of Shanghai IGI, new york IGI, Hong Kong IGI and India IGI, which are often contacted by diamond producers, the standards of each branch are different. Each branch has its own standards and local factors. Some are loose and some are strict, some are loose and unreasonable, and some are strict and unreasonable. Each branch has its own way and is not unified, which makes our producers and capable people know what their diamonds are like, when the certificate is issued, it is sent to the most favorable place for this diamond to be identified.
The characteristics of each identification system are divided by place: new york is stricter on color, looser on angle ratio, polishing and symmetry; India is looser on all grades; Shanghai is stricter on clarity, polishing and symmetry. The reason why the angle ratio, polishing and symmetry of new york in the United States are looser than those of other countries or regions is that the Jewish masters in new york use American horn jigs for cutting and grinding diamonds. For example, the tools used in mainland China are all Belgian system tools. Its bottom rotation angle has a lattice and is controlled very accurately. The master in new york fixed the diamond with two horns, grinded the first face at the bottom, and then grinded the second face on the opposite side, grabbed the diamond by hand and turned it to the opposite side, then looked at its parallelism to grind the second face, then grinded the third face by hand 90 degrees, and then grinded the fourth face by 180 degrees. The accuracy of the rotation angle of these four sides must not be accurate, so the appraisal institute in new york is not too strict with the angle ratio, polishing and symmetry of diamonds, because Jewish masters have been working all their lives, and they all think they are the world's sophisticated technology. If they fail to pass the certification, they are unwilling. Jews are very strong in diamonds, and every appraisal office must buy their accounts, so the angle ratio, polishing and symmetry of GIA's new york appraisal office are the loosest, but other parts of the new york appraisal office, like color, are stricter on average. The different standards in different places have caused considerable trouble to the diamond industry. The cultivated diamonds grown and cut in China are the most convenient to be identified in Shanghai, but the clarity, polishing and symmetry are too strict, which is unreasonable. As a result, many diamond industry companies have gone to great trouble to send them to the new york branch for certification.
6, diamond than color stone trouble
All appraisal offices have to deal with the prosperity and his big customers. The so-called big shops deceive customers and big customers deceive shops. They will also be oppressed by his big customers. He must buy what he wants to do. Take GIA as an example. When the prosperity is good, the standards will be stricter. When the prosperity is bad, GIA must adapt to the requirements of customers and relax the standards. Therefore, the standards set by GIA in those years later, with the prosperity of the economy, from the 1950 s to the present, there are about 70 years. As a result, all their standards are high and low, of which color is a very obvious situation. The color series of GIA certificates issued when the prosperity is good is relatively strict, and the color of certificates when the prosperity is poor is relatively loose, when the two diamonds are put together and compared, the difference in standards can be clearly seen. When GIA set it that year, it kept a set of standard bichromatic stones weighing more than 1 karat in the school-based department of Los Angeles, California, USA. This set of bichromatic stones was set by GIA that year and was very reasonable and strict. Later, the economy was not good many times. Up to now, GIA's standards, in my experience, have been loosened by one or two colors. In the world, only GIA has done the identification of colorimetric stones. GIA stipulates that this set of original 1 karat standard colorimetric stones must be used for comparison. We are very experienced in matching the whole set of colored stones. At that time, only one company called Laze Kaplan in the United States was doing it in the world. Because they grinded diamonds by themselves, they made colored stones and sent them to GIA for identification and matching. They sold them for many years. However, their factories no longer grinded diamonds with poor colors, so they only had high quality and could not make complete sets. At that time, I bought dozens of sets from them, in the end, they were left with about ten sets that did not match the complete set. We bought all the ten and a half sets. It took more than a year to select hundreds of them and send them to GIA. Only one by one, we sold them as soon as we matched them. This was about more than ten years ago, so the world could not buy new standard colored stones for natural diamonds for more than ten years. The problem of our cultivation of diamond color stone is more complicated, because natural diamond is a white and yellow system. The secondary colors of cultivated diamond except white are mainly coffee and gray, and some are a little green. Now no one makes diamond standard color stone. All the products available in the market are cubic zircon oxide. The accuracy of various color grades is very different. It is also a white and yellow system, which is used to identify white, coffee and gray systems, everyone's views are different, causing great distress. Take the white coffee system classification of natural diamonds as an example. At that time, when we were studying, we chose a set of natural diamonds with different shades of coffee system and sent them to different GIA graduate appraisers for identification. The biggest difference in results was about four color levels, because everyone's judgment direction was different. Some looked at how different the color of the diamond was from the yellow of the colored stone, some judged by light and shade, and some judged by color depth. Therefore, in the future, we must have two sets of standard white coffee system and white ash system for diamond cultivation. These two standards must be certified by credible institutions.
7. Potential Potential Diamonds
After the initial appraisal, the international formal appraisal company will notify the customer of the results. If there is a diamond with upgradeable potential, the customer is prepared to take it back and regrind it. The appraisal company will mark the improvable part of the diamond and return it to the customer for regrinding. This is an international practice in the appraisal community.
8. Each appraisal institute should determine and strive to maintain its own position.
All appraisal companies have their own positioning or recognized positioning in the market. Just like the two companies with competition in the region, market operators and consumers have knowledge of the standards of these two certificates. One is stricter and the other is looser. If the two appraisal companies also agree, everyone must try their best to maintain their consistent positioning standards and do not change the grading standards arbitrarily. Appraisal company is a kind of service industry, should try to do a good job of customer service. Water can carry a boat and overturn it. After the industry is not satisfied for a long time, it is possible to give up this appraisal and grading certificate in this area.
Related News
To participate in the "2011 Beijing International Lighting Exhibition" exhibition held in Beijing
Participate in the "7th Guangzhou International LED Exhibition (LED CHINA 2011)" exhibition held in Guangzhou
To participate in the "Japan International Electronic Products Exhibition" held in Tokyo, Japan"
Participated in the "Twelfth China International High-tech Achievement Fair" held in Shenzhen and won the "Excellent Product Award" certificate
Yuan Dong was invited to give a lecture at the Appraisal Institute of Taiwan Gemological Institute.
Dr. Yuan Zhizhong, Chairman of Bench Diamond Technology, gave a lecture entitled "Identification of Gem Diamonds Cultivated by CVD Method" at the Appraisal Institute on the 11.9 at the invitation of the Appraisal Institute of Taiwan Gemological Institute. In the lecture, Yuan Dong introduced in detail the historical principles of CVD diamonds and their development status, and introduced in detail several methods to distinguish CVD diamonds from natural diamonds on how to identify gem-grade CVD diamonds that participants are concerned about! Yuan Dong's wonderful speech was well received by the participants!
Yuan Dong Attends the Symposium at the Invitation of Hangzhou Jewelry City
Dr. Yuan Zhizhong, Chairman of Bench Diamond Technology, was invited by Hangzhou International Jewelry City to attend an academic symposium on November 19, 2013. At the symposium, Yuan Dong gave a speech entitled "International Situation and Identification of CVD Synthetic Diamonds" on the current situation of CVD synthetic diamonds that jewelers are concerned about and how to distinguish CVD diamonds from natural diamonds. In the speech, Yuan Dong introduced in detail the history of CVD diamonds, the international situation of CVD diamonds and the commonly used identification methods of CVD diamonds, and answered some questions raised by jewelers. Mr. Yuen's speech was well received by the participants, and all jewelers said they benefited.

